PERMUTATION LAST LAYER - PLL
There are a lot of algorithms to solve the Rubik's Cube introduced by
many people. Most are for the TOP layer.
those PLL algorithms use to solve a Rubik's cube with less time-consuming
than normal pattern.
Normally we take white as the base colour ( Down) then yellow will be the
TOP layer Upper side colour.
TOP Layer Algorithms:
How to make the TOP layer all pieces yellow on the upper side?
1. Need to make a Cross of the TOP layer
Use FRUR'U'F' when its a line from left to right

or
Use FURU'R'F' when it's an L shape from left to
back
When you have a fish shape in the top layer:
use R U R' U R 2U R'
The Cube must be like that when we do the above algorithm. if
no yellow colour facing the front and do the same algorithm twice ( with the
fish head towards left-front)
TOP layer Corner fix?
use R' F R' BB RF'R' BB R'R'
find whether the cube has headlights ( two matched edges and keep them
back when doing the above algorithm. if no headlights, keep comparing
right side to back and do the above algorithm until fixing corners are
(maybe twice)
Fixing Edges;
RR URU R'U'R'U'R' UR'
- for the clockwise rotation ( use when we need to move edges
clockwise)
RU' RURUR U'R'U' R'R'
- for the Anti-clockwise rotation ( use when we need to move edges
anti-clockwise)
swap opposite edges;
use 2M' U 2M' 2U 2M' U 2M'
PLL - PERMUTATION LAST LAYER - more!
Without a traditional TOP layer solution, we can use the following
algorithms to fix a cube without delay.
F
-Front B - Back
R - Right L - Left
U - Up D - Down
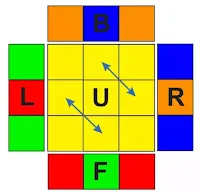
1. When we have imparity corners and edges like the below
image;
Hold the cube as shown by the notations and do the following
algorithm.
x (R2) F R F' R (U2) r'
U r (U2)
x - Rotate the cube along the
x-axis clockwise
r ' - Both middle and Rgiht Layers are to be rotated
anti-clockwise
Here, We need to swap the two corners of the right side and the two edges
of the right and the back sides.
The RIGHT-BACK corner is rotated clockwise and the RIGHT-FRONT corner is
turned anti-clockwise.
And, The right side edge moves to the back side and Vise-Versa.
for the less time-consuming, we have to practise more and more to solve
the cube as fast as we can and also need Hawkeye. otherwise, we will not
be able to see this pattern and go for the most time-consuming method that
we have already practised.
or keep blue side to back and do R' F R' BB RF'R' BB R'R'. then we will have a method once of the number 2 or 3.
The following are the most common practice methods used to solve a
Rubik's cube with more time-consuming but not always. we used some
algorithms to make numbers 2 and 3 methods and use those algorithms then
to solve.
By using the " R' F R' BB RF'R' BB R'R'
" algorithm one time or a few times, we get the cube in the form of the
following number 2 or 3 methods.
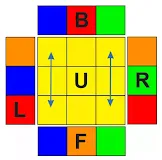
2. When we have imparity edges like the below image;
We use this method when we solve a cube in Corner First then the
Edges method.
by keeping one correct corner to the right-back or both correct corners to
the back and using R' F R' BB RF'R' BB R'R'. we get this position.
Here all colours are matched in the backside. for the right, front and
left sides, the edges need to move along the clockwise rotation which
means, the Red piece needs to
move towards the right side, the
Green piece needs to move
towards the front side and the
Orange edge piece needs to
move towards the left side.
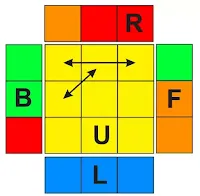
3. When we have imparity edges like the below image;
This is the exact opposite of number 2, the Anti-clockwise movement of
edges to fix the cube.
as shown in the figure, the
Orange edge moves to the
left, the Green edge moves
to the front and the Red edge
moves to the right when we do the above algorithm.
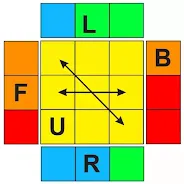
4. When we have imparity edges like the below image;
2M' U 2M' 2U 2M' U 2M'
Sometimes we will have imparity like the above image. opposite edges
swapped each other ( Green-Blue and Red-Orange).
Either we can use 2M' U 2M' 2U 2M' U 2M' to fix at once
or
use R' F R' BB RF'R' BB R'R' if you hard to remember so many patterns and algorithms, it will redirect again to method 2 or 3.
but it is more effortless if you remember the
2M' algorithm than
others.
5. When we have imparity corners and edges like the below image;
|
|
2R F (R U R U’ R’) F’ (R U2 R’ 2U' R U)
|
If you ever have something like the above image when solving a cube,
use the algorithm mentioned above to fix the cube at once. or
use R' F R' BB RF'R' BB R'R' to fix
click here
to see how with details.
Here two corners of the right side need to swap, while swapping them,
the right-back corner rotates clockwise and the front-right corner
rotates anti-clockwise. meanwhile, the front and the left edges are
swapping each other to fix the cube.
6. When we have imparity edges like the below image;
If we come across imparity edges like the above image when solving a
cube, need to use a special algorithm like
R' U' R U' R U R U' R' U R U (R2) U' R'
to solve it.
or
use R' F R' BB RF'R' BB R'R' to fix click here to see how with details.
Here we got edges swapping positions but not opposite. instead, we have
to swap the front - the left edges and the right-back edges
simultaneously.
The back and the Front takes clockwise rotation and the right and the
left edges take anti-clockwise rotation.
7. When we have imparity corners like the below image;
xR2D2 RUR' D2 RU'R x'
in No:7, only 3 corners have an
issue with imparity and are willing to move along an anti-clockwise
rotation as shown in the above image.
The Red-Blue-Yellow corner should move to the Front-Right corner, the
Orage-Blue-Yellow corner towards the Right-Back corner and the
Orange-Green-Yellow corner to the Back-Left corner ...
As shown in the image, two corner colours are matched on the right
side. keep them as it is, and do the above-mentioned algorithm to fix
the cube.
or keep them ( two matched colours) on the back
and use
R' F R' BB RF'R' BB R'R'
once to a few times to match all corners. then we can use No2 or 3
algorithms to fix the cube.
8. When we have imparity corners and edges like the below
image;
xR'UR' D2 RU'R' D2R2 x'
exactly opposite algorithm than in No.7. and the movement to edges also.
here Clockwise rotation needs to fix the cube by using the above
algorithm.
The Orange-Blue-Yellow corner is towards the Back-Left corner. the
Red-Blie-Yellow corner to the Back-Right corner and the Green-Red-Yellow
corner to the Front-Right corner...
9. When we have imparity corners like the below image;
x'
(RU'R'D) (RUR') (D'R) (UR'DRU'R'D')
x
No double corners are matched. but it is easy to fix using the
above-mentioned algorithm. Keep the yellow side up and rotate the whole
cube along the x-axis anti-clockwise.
The green-Red-Yellow corner piece and the Orange-Blue-Yellow move
anti-clockwise and The Orange-Green-Yellow and the Blue-Red-Yellow pieces move
clockwise when following the above algorithm.
10. When we have imparity corners and edges like the below
image;
Following T-perm is
found sometimes when We going to solve a Rubik's cube.
(RUR'U'R') F (R2U'R'U') (RUR') F'
Here, two corners of the TOP-Front-Right and the TOP-Right-Back are
swapped. and Edges of the Left and the right also swapped.
We can swap the mentioned corners and edges simultaneously by doing the
above algorithm (The yellow colour should be up when using the algorithm).
11. When we have imparity corners and edges like the below
image;
(R’ U’ F’)
(R U R’ U’ R’)
F
(R2 U’ R’ U’ R U R’)
U R
Keep the solved edge, and corners to the left side then, imparity edges
and corners are in the front and the back.
Then, do the above algorithm to fix the cube.
when doing the algorithm, the opposite edges of the Front and the back
will be swapped. meanwhile, the front-Right corner and the back-right
corner will be swapped(the front corner rotates anti-clockwise, back
corner rotates clockwise).
12.a. When we have imparity corners and edges like the below
image;
J-permutation or J-perm
R U R' F’ R U R' U’ R’ F R2 U’ R’ U'
J perm is one of the PLL methods for an easy solution to a Rubik's cube. By
using the above algorithm, we can fix the upper layer at once. Hold the cube
as shown above image, and use the mentioned algorithm once. two imparity
corners of the right side will be swapped and the edges of the front and
right sides also swapped simultaneously.
when the cube holds like above, we can see only the left side is fixed and
one corner of each other side is not placed correctly but actually, only two
corners of the right side and two edges of the front and the right sides are
moved with the algorithm used.
’ U L’ U2 R U’ R’ U2 R L
12. b. When we have imparity corners and edges like the below image;
R’ U L’ U2 R U’ R’ U2 R L U'
This is the exact mirror image of the above 12. a when (vertically
flipped image- only imparity corners and edges.) other colours are not
much important. but the algorithm is not a mirror or opposite as used in
12. a
But there should be a slight difference when we going to use the
algorithm, if the cube holds the above and used the algorithm, the cube
will not be fixed, instead same type of imparity with different colours
will be got.
So, If we want to fix this arrangement, the cube should be held like the
image below.
Keep the all-matched colour to the Front side and use the algorithm to
fix the cube at once.
13. a.When we have imparity corners and edges like the below image;
There are two types of similar arrangements which are exactly
opposite mirror images.
a.
(R’ U2 R U2 R’) F (R U R’ U’ R’) F’ (R2 U')
shows the back side corners are swapped and the left and the edge of the
Front side also. let the cube-like above and follow the algorithm
mentioned above we can fix the cube.
b.
This is the exact mirror image of part a.
Use the following algorithm to fix the cube.
y R U’ R’U’ R U R D R’ U’ R D’ R’ U2 R’ U'
y - Rotate the whole cube along the y-axis clockwise once.
and then, it will show like the below image;
If the cube does not rotate along the y-axis, the algorithm should be
like this;
B U’ B’U’ B U B D B’ U’ B D’ B’ U2 B’ U'
R is replaced by B, if the cube rotates along the y-axis, B becomes
the Right and it will easy to rotate the cube than if not.
14. When we have imparity corners and edges like the below
image;
F R U’ R’ U’ R U R’ F’ R U R’ U’ R’ F R F'
Here, pieces are swapped just like a cross angled to the left. the corners
of the Front-Right and the Back-Left are swapped. and edges of the
Left and the Back also swapped. also known as Y permutation or Y perm.
hold the cube as shown in the above image. then, Use the above algorithm
to fix the cube.
15. When we have imparity corners and edges like the below
image;
F'UF'U' y F'L'F2 U'F' U F'L FL
or
Turn the cube anti-clockwise and it will show like the below image
Then use the below algorithm to fix the cube
R’ U R’ U’ y R’ F’ R2 U’ R’ U R’ F R F
or use the below algorithm
R’ U R’ U’ B'R' B2U'B' UB' RBR
By keeping the cube as the second image shown, it is easier than the
first one.
And R’ U R’ U’ y R’ F’ R2 U’ R’ U R’ F R F
is a very easy algorithm to use than others.
16. When we have imparity corners and edges like the below image;
It is called a diagonal corner swap or N-permutation.
There are two main possibilities.
a If the Rubik's Cube TOP layer has corners and edges that are imparity
like the above image, that is Edges of the Left and the Right, as well
as corners of the Front-Left and the Back-Right are swapped.
R U R’ U R U R’
F’ R U R’ U’ R’ F
R2 U’ R’ U2 R U’ R’
b. If the Rubik's Cube TOP layer has corners and edges that are imparity
like the above image, that is Edges of the Left and the Right, and
corners of the Front-Left and the Back-Right are swapped.
R’ U R U’ R’
F’ U’ F R U R’ F
R’ F’ R U’ R
The above two are opposite mirror images of each other but the algorithms
are not much different.
17. When we have imparity corners and edges like the below image;
Corners and edges are rotated simultaneously, also called
G-Permutation. There are a few different scenarios with this permutation.
a. Corners need to move clockwise and edges need to move
anti-clockwise. It is very hard to gather for the first time unless we
have a good experience with these movements.
R2 U R’ U R’ U’ R U’ R2 U’ D R’ U R D’
b. It is so similar to part a. The only difference is that the
movement of the edges is exactly opposite to the above part a. and the
algorithm is also the opposite of the above one.
D R' U' R D' U R2 U R' U R U' R U' R2
c. It is another imparity permutation,
in which is 3 corners and three edges move simultaneously but in opposite
directions. Two Front side corners with the Back-Left corner moving
Anti-clockwise with the front, the Left and the Back Edges moving
clockwise.
R’ U’ R U D’ R2 U R’ U R U’ R U’ R2 D
d. Here we have another Permutation issue.
Two Front side corners with the back-left corner which is misplaced with
anti-clockwise movement. Also, the Front, the Left and the Right edges are
also misplaced with clockwise rotation.
Corners and edges move in opposite movements with the following algorithm
in order to fix the cube simultaneously.
R2 U’ R U’ R U R’ U R2 U D’ R U’ R’ D
R2 U’ R U’ R UR’ U R2 U D’ R U’ R’ D
e. Here, We
have another situation that two backside corners with one Front-Left
corner and the Front-the Back and the Left edges are misplaced with
clockwise rotation of corners and anti-clockwise rotation of edges. R2 HereU’ R U’ R U R’ U R2 U D’ R U’ R’ D
R U R’ U’ D R2 U’ R U’ R’ U R’ U R2 D’
It is not so easy to get on the first try. need to focus and practice for
better improvement of speeding to solve with this type of algorithm,
otherwise, it will be more time-consuming than the basic method.
There are the most difficult algorithms to remember because of two
movements at the same time. so, which algorithm that we need to use for
fixing the cube, is just for luck when solving the cube.
18. When we have imparity corners and edges like the below image;
diagonal edge pairs swapped each other. The Front - Right and the Left-Back
edges have been swapped.
2M U 2M U M’ 2U 2M 2U M’ 2U
or
2M' U 2M' U M’ 2U 2M' 2U M’ 2U
By using the above algorithm, it is so easy to fix the cube.
We can use both algorithms but I prefer the second one. Because it is easy
to rotate the anti-clockwise rotation of M than the clockwise
rotation.
There are so many algorithms mentioned here that are helping to resolve TOP layer corner and edge issues in a Rubik's Cube.










%20F%E2%80%99%20R%20U2%20R%E2%80%99%20U2%20R%20U.webp)



.webp)














No comments:
Post a Comment